Many people believe that a warm and durable country house can only be built from brick or logs. This is not true. A modern frame house, built in compliance with technology, will last up to 150 years, and it will not be cold in it. We understand the features of building frame houses.
What is a frame house
A classic frame house is a house that is based on a wooden frame, where all the load-bearing elements are interconnected. The frame is filled with insulation, vapor barrier, and other insulating materials. Interior and exterior decoration in a frame house is usually made of wood or materials that imitate it, for example, false beams or block house boards.

Frame houses are built quickly and cost 20–30% less than houses made of brick or aerated blocks. But this does not mean that such a house is short-lived or does not retain heat well. A properly built frame house will last up to 150 years. The heat loss in it is several times less than that of a house made of brick or aerated concrete, and it heats up faster.
Basic rules for building a frame house
The service life of a frame house directly depends on the quality of the materials. Two rules should be followed during construction so that the result does not disappoint:
- Dried board only. Frame houses should only be built from kiln-dried wood. The board should be planned, not edged. It costs more than similar lumber with natural moisture, but the house will not move or warp over time – such defects cannot be eliminated later. In addition, properly dried wood is less susceptible to mold and mildew.
- High-quality building materials. You should not skimp on insulation and fasteners. To build a frame house you will need a lot of insulation, and it is not cheap. It may be tempting to buy the cheapest mineral wool so that you have more money left over for finishing, but you don’t need to do that. The house will turn out cold, you will have to heat it more often, and it will not last long. The same goes for fasteners: cheap corners and plates made of thin metal may not withstand the load – and the structure will collapse.
What is needed to build a frame house
In addition to boards, fasteners, and insulation, many other materials and elements will be required to build a house. To better understand the specifics, let’s look at what a frame house consists of from the foundation to the roof, and we’ll tell you what materials are best to use.
For the foundation
A frame house is much lighter than a brick or block house, so it does not require a massive concrete foundation. Except for cases when it is necessary to build on unstable, moving, and subsiding soils. If everything is in order with the soil, the best option is a pile foundation. It comes in two types: on screw piles and driven piles.
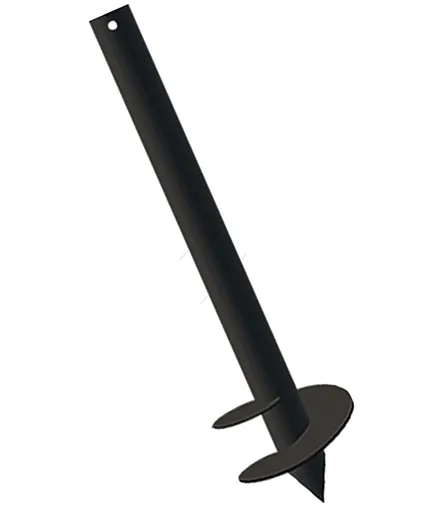
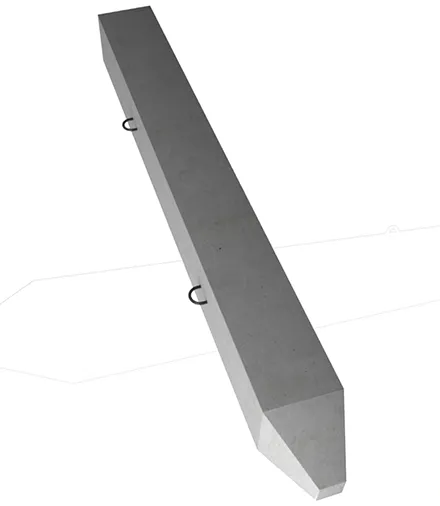

In terms of reliability, the advantage here is on the side of driven reinforced concrete piles. They are quickly installed and are better fixed in the ground than screw ones. When driving them, the soil is not removed, but pressed, compacting around the pile.
The final decision on what type of foundation to use must be made taking into account the geology of the site and the budget. For example, a screw foundation will be cheaper, but if the soil is damp and unstable, the house may collapse.
For frame
Coniferous wood is most often used for the frame of a house. Spruce and pine are ideal materials for a frame house. The trunks of these trees are smooth, with a small number of knots. Conifers also have a high natural resistance to decay and can be treated well with antiseptics.
Depending on the type and complexity of the structure, lumber of different sizes is used. For pillars, mats, and framing you need timber 150 × 150 mm or 200 × 200 mm, and for frame racks – boards from 20 × 100 mm to 50 × 200 mm. For crossbars, 35 × 35 mm timber and smaller slats are suitable.
For insulation
The thickness of external walls in frame houses can vary from 200 to 300 mm. In northern regions, more insulation is required to reduce heat loss. The thickness of the internal walls rarely exceeds 150 mm.
The design of the walls resembles a multi-layer cake. In addition to insulation, external cladding, and interior finishing, a membrane and vapor barrier are installed inside in a certain sequence:
- External facade cladding – any material for exterior finishing (facade board, imitation timber, or tile).
- The membrane protects thermal insulation from wind, water vapor, and water from the outside, and also removes moisture that can enter from the inside.
- The insulation provides thermal insulation. This can be basalt mineral wool, fiberglass, or quartz wool.
- Vapor barrier is a rolled non-woven material made of polypropylene and a thin layer of foil. Needed to prevent moisture from getting inside the insulated wall.
- Interior finishing is usually lining, imitation timber, or sheet material, such as plasterboard.

For roofing
The roof consists of a rafter system and roofing covering. A board of 50 × 100 mm or 50 × 150 mm is usually used as rafters. Softwood lumber is best suited.
If the house has a residential attic, the same pie method is used to insulate the roof as for insulating the walls. Only instead of a façade board they put soft tiles, corrugated sheets, or other roofing material. It is not recommended to take clay and clinker tiles. It’s too heavy. The weight of such tiles can cause the frame of the house to deform.
For exterior decoration
The facade of the house can be finished with facade boards, imitation timber, flexible tiles imitating brickwork, or any other available material. The choice depends only on your wishes and budget. You can often find frame houses covered with vinyl siding.


Frame construction technologies
Today, there are two technologies for constructing a frame house: classic and panel (SIP). They are united by the advantage of the speed of construction. If it takes at least a year and a half to build a log house, then a frame house can be built in a few months.
Classic frame construction technology (Finnish)
The structure of a frame house is assembled locally on the foundation – these are racks made of coniferous wood and frames. The frame is lined with insulation, covered with wind and moisture protection, and covered with facade boards.
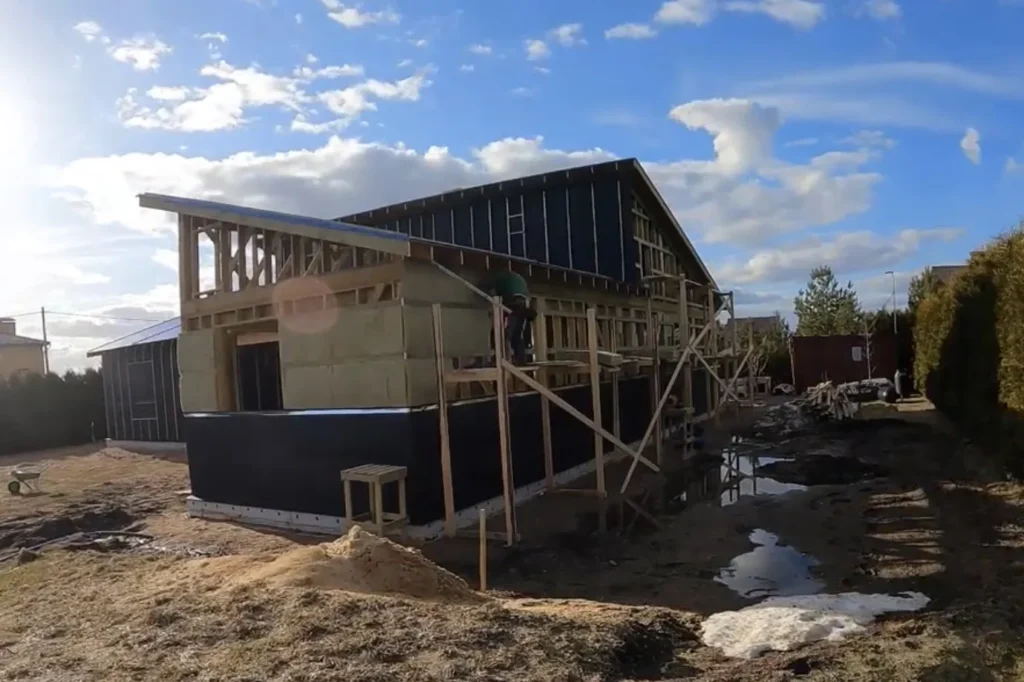

Houses using Finnish technology are built slower than panel houses, but they are warmer and more environmentally friendly. During the assembly process, you can control the quality of materials, add insulation where necessary, and lay utility lines inside the walls.
Read more: Seven types of insulation for the home: which one to
Panel technology of frame construction
In this technology, the frame house design includes thermal insulating SIP panels. This is a sandwich of two OSB boards and insulation made of non-combustible material between them. SIP panels are manufactured in production, then the finished structures are delivered to the site and attached to a wooden frame.
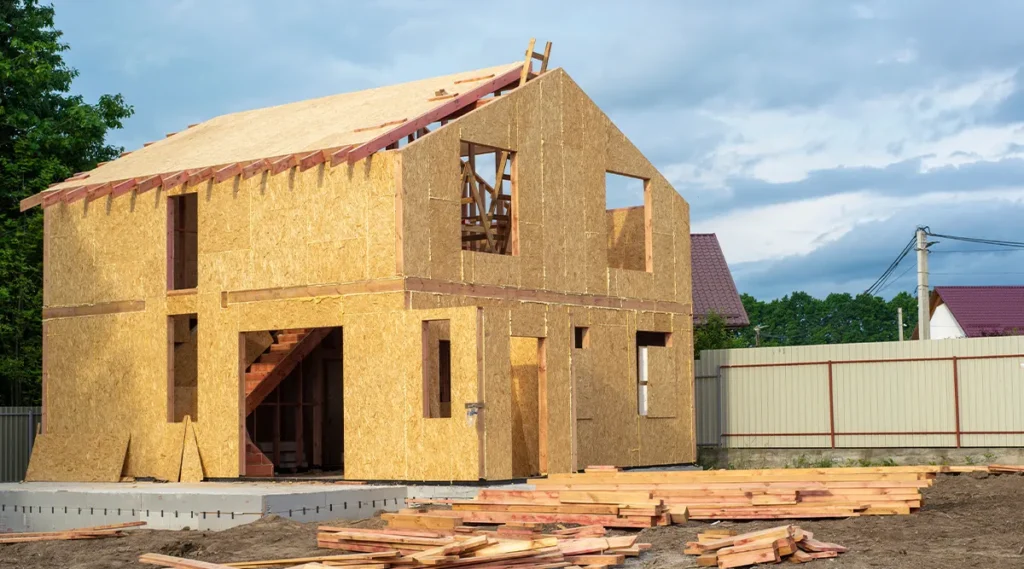
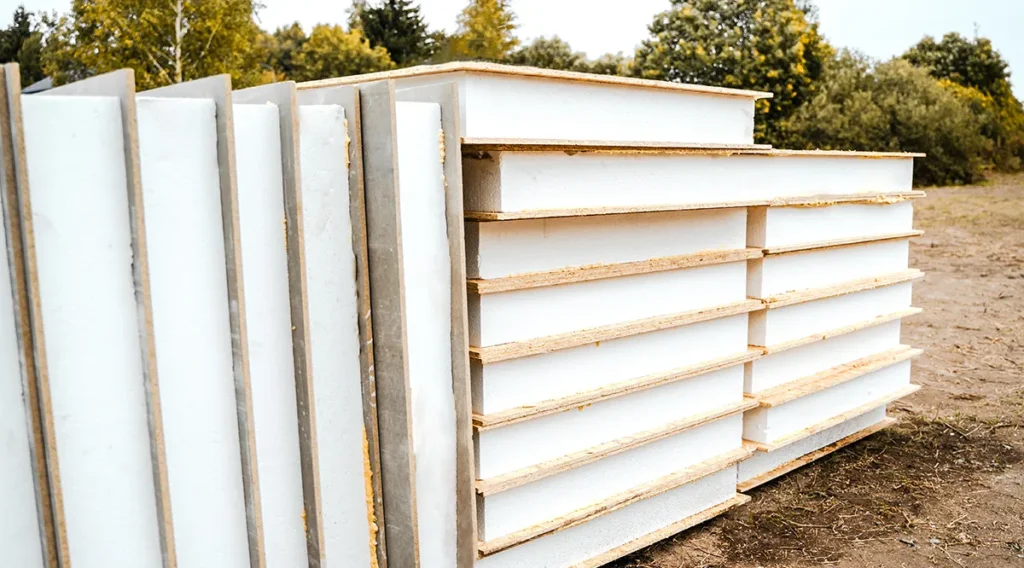


This method of building houses is the fastest, but living in them is not always comfortable. Expanded polystyrene is most often used as insulation in SIP panels. When it is heated, for example on hot summer days, harmful fumes may be released.
The main stages of building a frame house
Choosing a location on the site
Before you start construction, plan the site. It is necessary to take into account fire and sanitary standards, as well as the red building line. Pay attention to indents from communications, and neighbors. In addition, an important factor is solar insolation. To keep your house light all year round, look at how the sun moves and how the house will be illuminated.
Read more: HOW TO POUR A FOUNDATION FOR A HOUSE WITH YOUR
Construction of the foundation
Before preparing the foundation, the area must be cleared of debris, stumps, fertile soil, and leveled. If the terrain is uneven or the site is located in a lowland, additional backfilling of the landscape or drainage work must be carried out. Only after this can you begin to build the foundation.
The site for building a house is marked and small recesses are prepared for the piles to guide the point. The pile-driven foundation is installed using a pile driver – a special pile-driving machine.
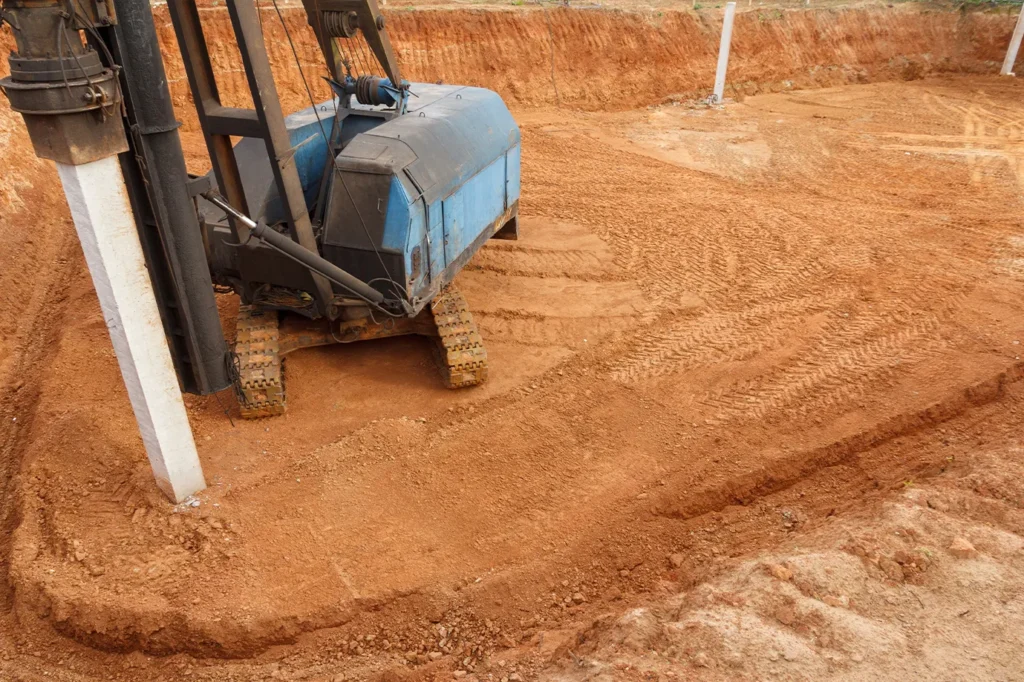

Typically, the depth of driving piles is from 2 to 8 m. It can vary depending on the type of building and the characteristics of the soil. To figure out at what depth to drive piles, you need the opinion of an experienced geologist.
Bottom strapping and laying of floor coverings
To start building walls, you need to prepare a foundation for them. This role is taken on by the lower harness. Usually, it is made from a set of boards or timber 150 × 150 mm or 200 × 200 mm. The lumber is laid on the foundation through a waterproofing flashing to prevent rotting. The beams are securely attached to the piles and each other using staples and screws. The joints are sealed with jute or polyurethane foam.
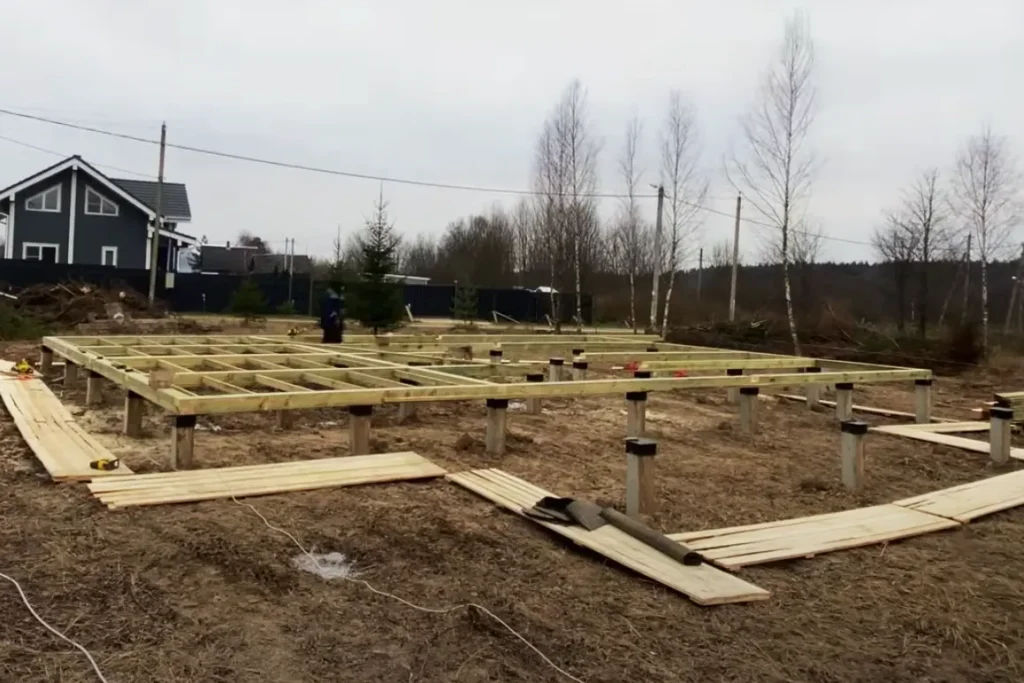

After the piping is completely ready, you can begin the first stage of arranging the subfloor. Usually, they make a sheathing from a board, which will serve as the first layer of the insulated floor pie. The second stage – installation of insulation, waterproofing, and vapor barrier – must be started when the house is already under the roof so that moisture does not get into the floor.
Construction of the frame
The frame is assembled directly at the installation site of the future wall in a horizontal position. Then the structure is lifted manually or using a winch.
You need to start assembling the frame with the corner posts. The remaining vertical beams are mounted between the corner beams at a distance of approximately 600 mm. The pitch depends on the insulation board.
Then horizontal beams are installed, which should close the contour of the wall, giving the structure the necessary strength. If there is a window in the wall, you need to prepare an opening.

When all the walls are assembled and securely fastened, you can begin to frame the top. It must be made from timber of the same size that was used in the lower frame. The timber is laid along the contour of the future house and securely attached to the horizontal beams of the walls.
Installation of rafters
To form the roof, a system of rafters from boards with a section of 50 × 150 mm or 50 × 200 mm is used. The thickness of the board and the installation pitch of the rafters must be selected depending on the size of the house. For example, if the length of the roof slope is 5 m, the rafters should be placed at a distance of 600 mm from each other. If the house is small, the distance between them can be increased.
It is more convenient to install rafters directly on the roof. This way you won’t have to lift heavy structures.
Final works
Once the wall frame and roof are ready, you can begin installing the insulation. Mineral wool slabs must be tightly inserted into the wall frame between vertical and horizontal boards. Cover the outside walls with a waterproofing membrane and press them with counter-battens. Cover the inside with a vapor barrier film and cover with interior trim.

The same operations must be done with the floor and roof. The structure differs little from the walls – you can use the same insulation, film, and membrane.
Next comes the installation of windows and doors, communications, exterior cladding, and finishing inside the house.
Read more: What is the best roofing material for a home?
Advantages and disadvantages of frame technology
The mass construction of frame houses has been going on relatively recently, but people have already managed to appreciate all the advantages and disadvantages – they couldn’t do without them either.
Advantages
- Low cost. Construction of a frame house will cost 20–30% less than houses made of brick, logs, or any other material.
- Speed of construction. A typical house using frame technology can be built in 1.5 months, while other technologies require more time.
- Heat capacity. A properly built frame house warms up quickly and retains heat for a long time.
Disadvantages
- Assembly feature. When constructing frame houses, it is necessary to strictly follow the technology. Otherwise, the house will not last long.
- Need for ventilation. In a frame house, the insulation loop is closed the walls are insulated and lined with hydro- and vapor barriers, so the house does not breathe.
Examples of frame houses
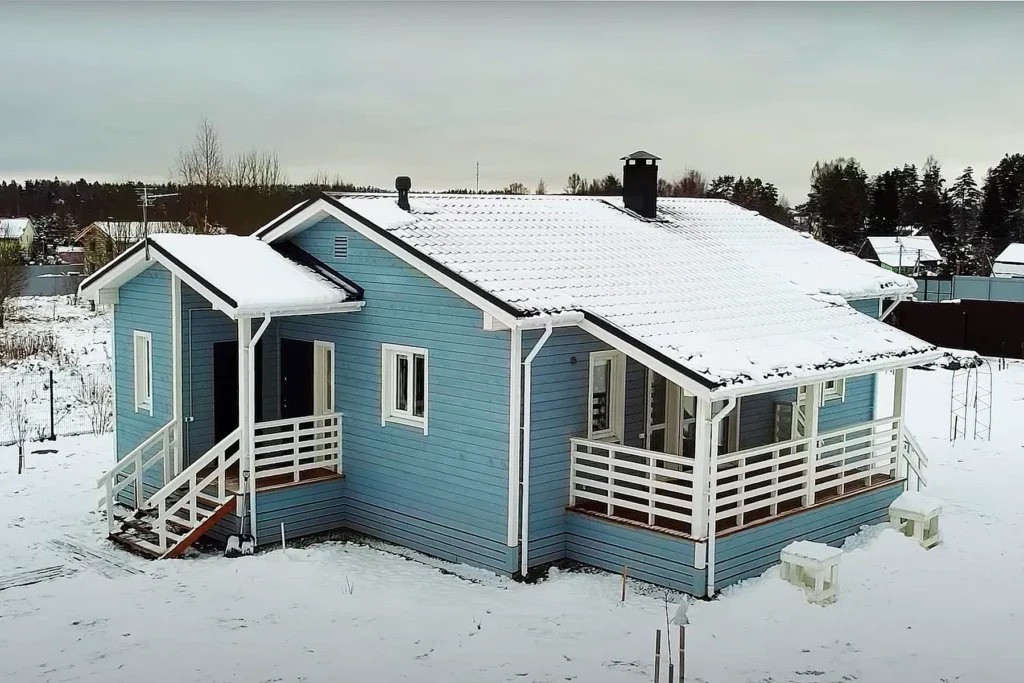
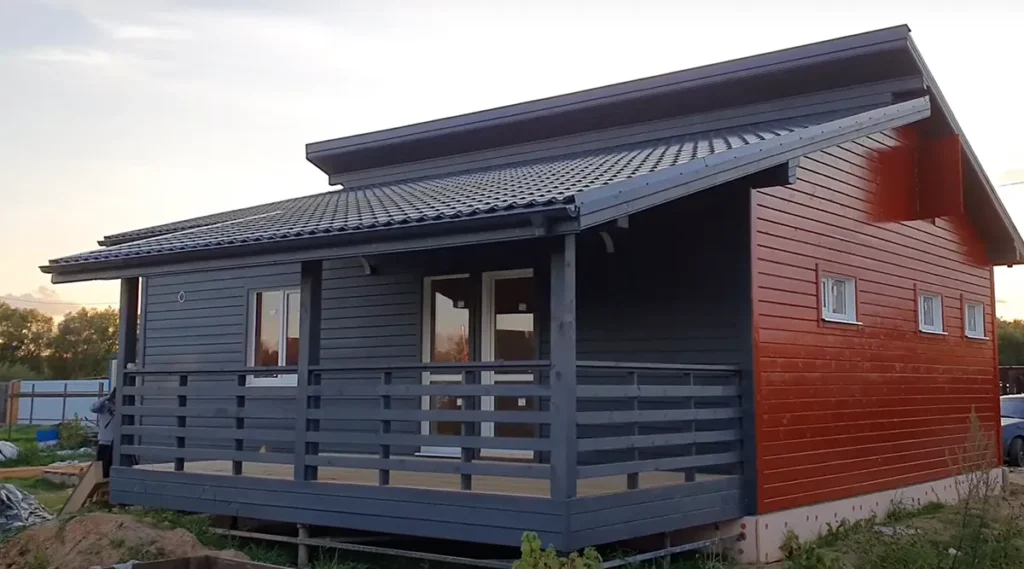
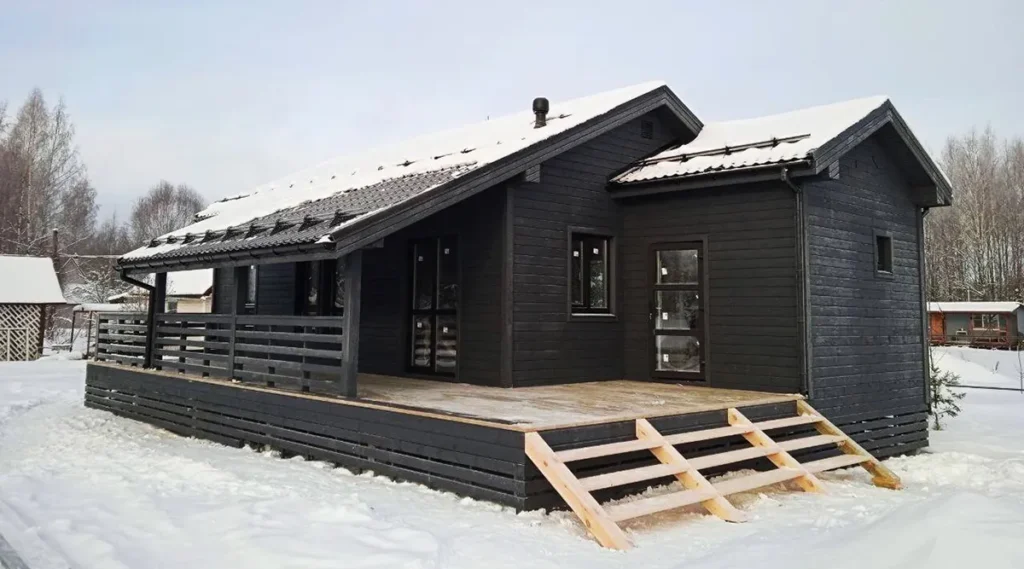
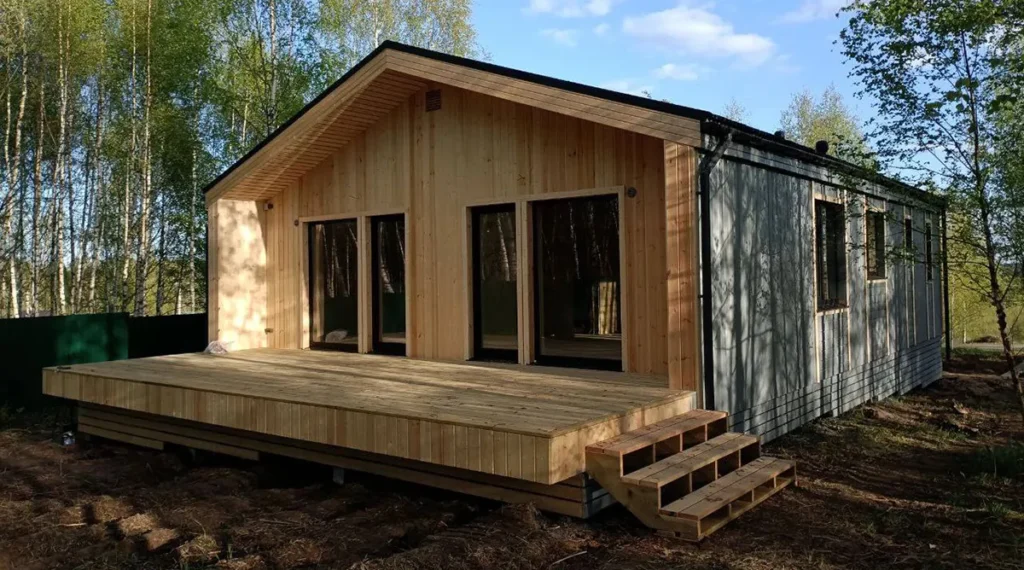
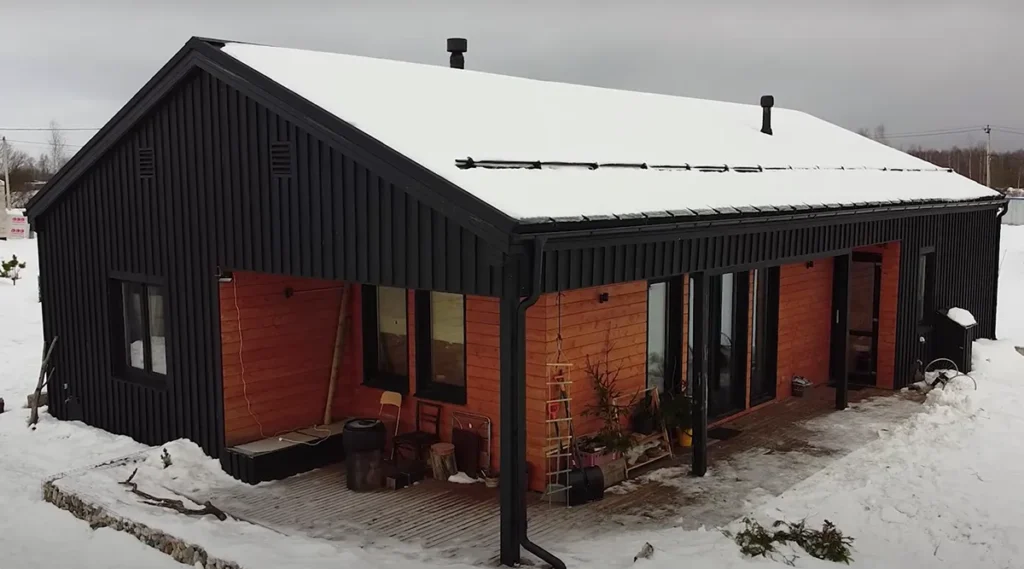
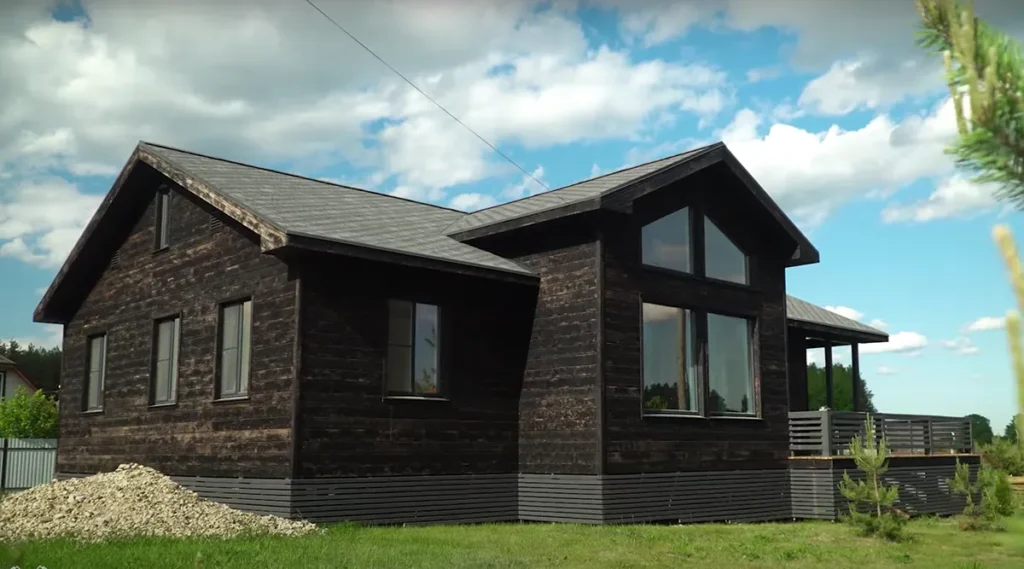
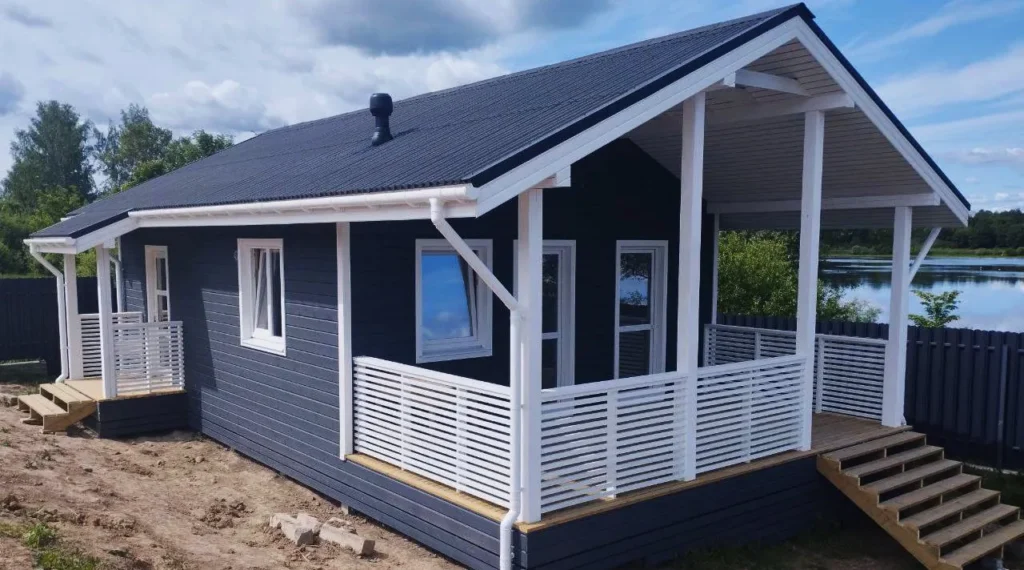







Summary
It is quite possible to build a frame house yourself. But if you decide to take such a step, study the technology and prepare a detailed project – this will help you calculate the volume and quantity of materials needed. Purchase materials in stages and do not skimp on quality lumber and fasteners.
If you decide to turn to a construction team, then find one that has already built more than one frame house. Do a little research: study reviews look at houses that have already been built by these specialists. Chat with the owners of the houses. This will help you find out how accurately the team follows the technology of building a frame house and will protect you from negative experiences.
Read more: Aerated concrete house – to build or not? Advantages and disadvantages



