A frame can be built quickly, without interruption even during the winter, and you can get a warm house for permanent residence. But are there any downsides? Of course yes. We analyze all the advantages and disadvantages in the article.
According to the largest manufacturers of mineral wool and polymer insulation, today the share of frame houses in low-rise construction in Europe has exceeded 60%. Is this fashion, a consequence of aggressive advertising, or does the trend have objective reasons? Perhaps the main players in the building materials market somewhat exaggerate the popularity of frame frames, and yet it is difficult to deny that they are being built more and more often, mainly for permanent residence. So, in the article we analyze all the pros and cons of frame houses and also share the opinions of experts.
Features of the technology
A modern frame building is no longer the same country frame-panel house, the pros and cons of which we will not discuss: how can we talk about the advantages if there is blowing from all the cracks and even with slight frosts the rooms are instantly cooled.


You need very little wood to build a house (4-6 m3), and insulation and films are quite affordable, they have become much more durable and easy to use than 15 years ago. There is no risk that you will receive defective bricks or blocks; it is easier to avoid the difficulties associated with raw lumber (it is best to buy kiln-dried boards – this will not increase the estimated costs too much).
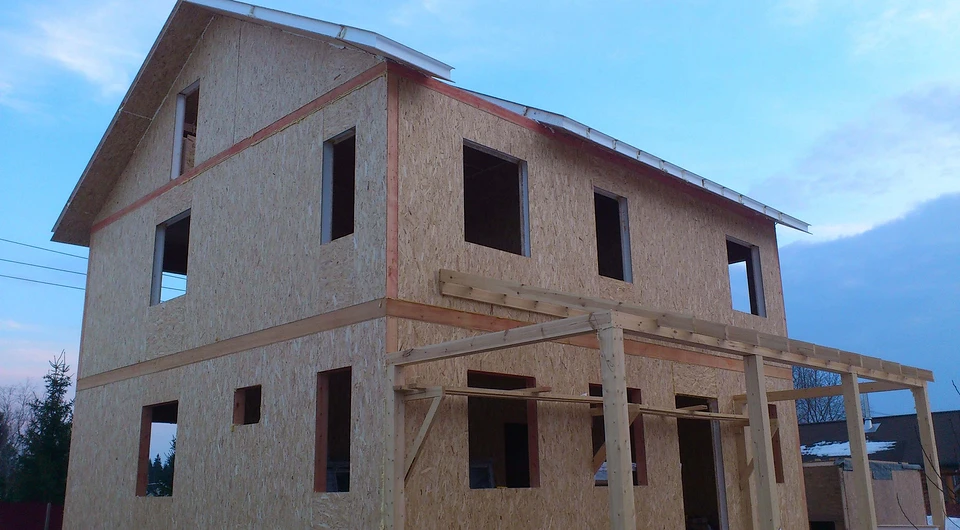

Advantages of frame houses
Light weight of walls and ceilings
Lightweight structures do not need a powerful concrete foundation. For budget construction, you can get by with a pile-drilled or pile-screw foundation, although it is still better to pour an insulated slab. Where a stone house would require a slab with a thickness of 300 mm or more, for a frame house 100 mm with fins with a height (depth) of another 100 mm is sufficient.
Good thermal insulation
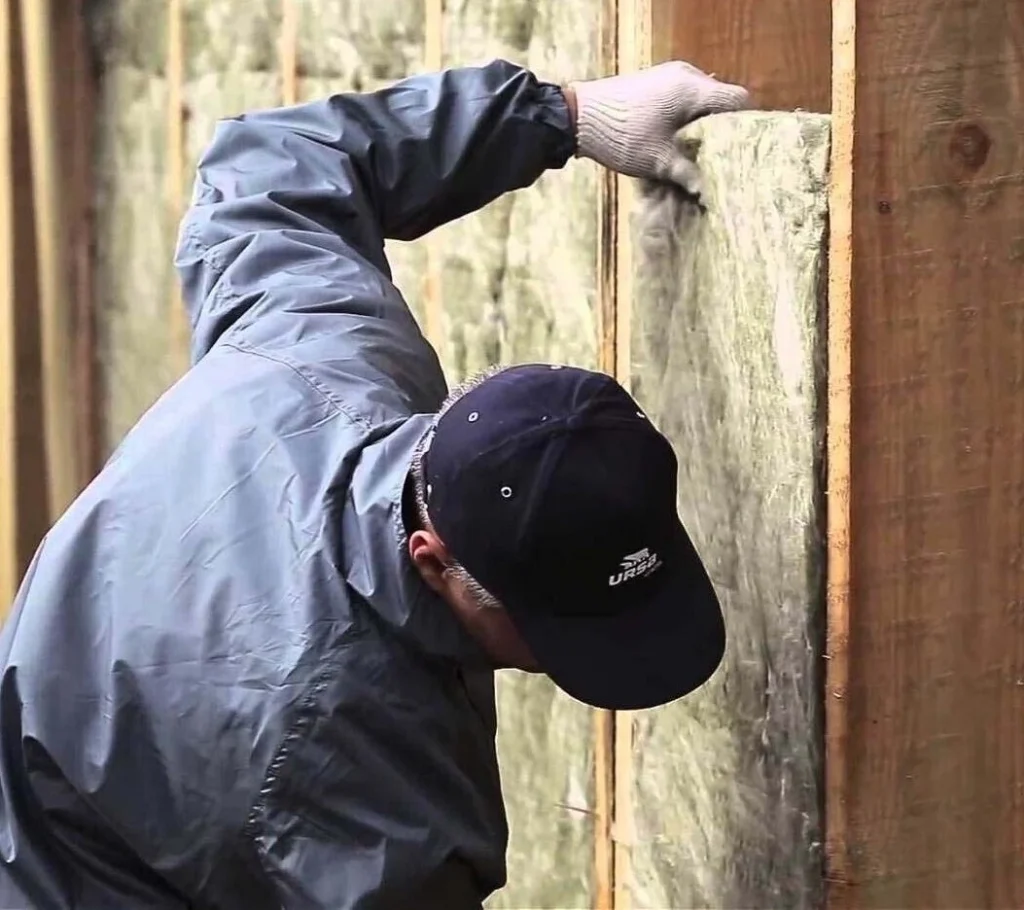
The main element of frame fencing is insulation, because heat transfer resistance and sound insulation depend on it. Most often, stone and glass wool are used, pressed into rectangular slabs. Thanks to special additives, such products do not shrink.
A wall insulated with mineral wool 200 mm thick has almost twice the heat transfer resistance of a wooden wall of the same thickness. In practice, only the use of effective insulation materials makes it possible to meet modern heat conservation standards. Another thing is that good thermal insulation is not enough to make the microclimate in the house comfortable.


High construction speed
To build any other house (including the production of a house kit), it will take at least six months. A frame with an area of 150 m2 will be ready in 3 months, and you will not need either powerful lifting or other equipment, or a large team – three or four people are enough. In principle, you can build it yourself, with the help of one family, the main thing is to prepare thoroughly and collect as much information as possible.
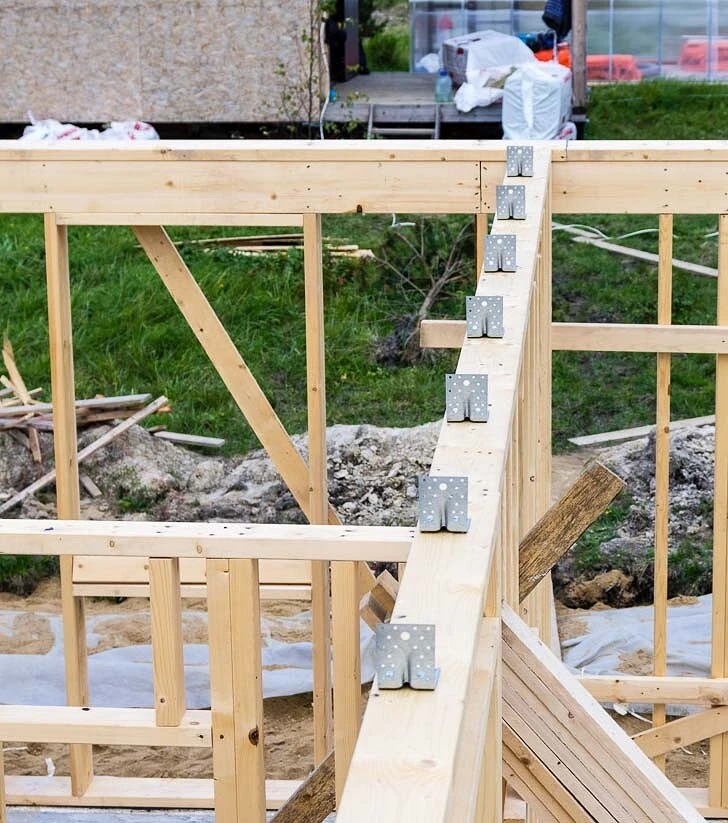

Possibility of crew work during the cold season
Frame walls are easy to assemble at any air temperature – you just need to avoid wetting the insulation and frame parts. A pile-screw foundation can also be installed in winter. This all-season nature allows you to save money, since in winter prices for construction services are slightly reduced due to a drop in demand.
Based on the above, it would seem that the answer to the question of whether it is worth building a frame house is obvious. But this technology has disadvantages.
Disadvantages of frame houses
The main disadvantage is related to the microclimate, or more precisely, the difficulty of maintaining optimal levels of humidity and oxygen content in the air. The sealed wall does not let in outside cold but does not let humid air out of the premises. Due to high humidity, the perceived temperature inside without properly organized ventilation is always lower than the actual one. Modern heating systems with forced air convection and supply ventilation devices (windows, walls) can partially solve the problem. And the most effective supply and exhaust systems with heat recovery. However, for installation of such a system in a house with an area of 150 m2 will be expensive. (in this case, it is necessary to provide in advance a place for placing air channels).
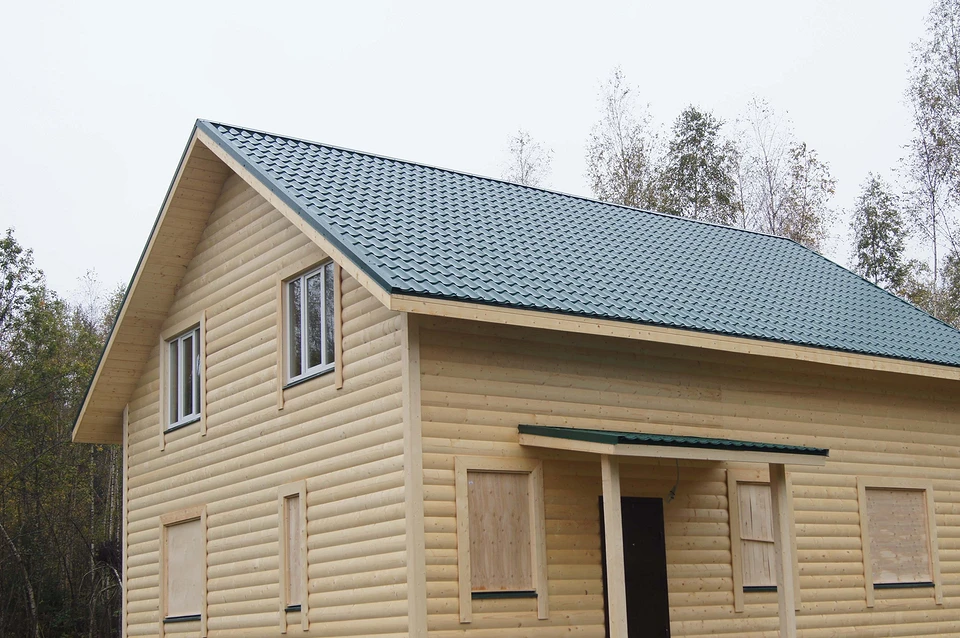

Another disadvantage is the relatively short service life of the building, mainly due to the properties of the insulation. To build a winter milkhouse with a service life of more than 40 years, you must select only high-quality materials and follow the rules for their installation. However, the feasibility of building a “house for centuries” is in doubt these days: architectural fashion is changing too quickly, and the priorities of generations diverge too much.
When the pros and cons of frame houses are discussed on construction forums, reviews are often written about rodents that allegedly live inside the walls. They mostly talk about SIP panels, since mice do not live in mineral wool. So, with proper construction, that is, the absence of voids, cracks, and gaps in the walls and ceilings, mice threaten the frame no more than any other building.
Prices
The price of a house is determined not so much by materials as by other factors, the main one of which is the quality of construction. In addition, the relevance of the project, the level of engineering equipment, and finishing play an important role. Therefore, a frame house may cost more than a log house, but only the first will be built according to modern rules, and the second will be built according to outdated technology, carelessly, with savings on everything except wall material.
On the other hand, there are extremely cheap options on the market in the so-called minimum configuration. However, such a house is unlikely to please the customer: it will have low ceilings, poor heat and sound insulation, primitive engineering systems, and poor finishing. Meanwhile, upgrading a building to an acceptable level is difficult, unprofitable, and often completely impossible.

Frame principle in multi-story construction
In mass urban construction, panel high-rise buildings have been replaced by monolithic frame houses, the pros and cons of which are still far from obvious. The essence of the building design is that first, using the monolithic casting method, a supporting frame is made of racks (or internal partitions) and ceilings, and then the façade openings are filled with light blocks. To avoid freezing on the concrete frame parts, thermal liners, and a warm curtain façade are installed. The main advantage of such houses is their low cost, so new apartments have become a little more affordable. Thermal insulation is also almost always good, but inter-apartment partitions sometimes allow airborne noise to pass through (much depends on the conscientiousness of the developer). There are heated debates about the service life of such houses: many architects and builders believe that in 30-50 years, frame-monolithic buildings will require expensive replacement of the facade and major repairs of communications.



