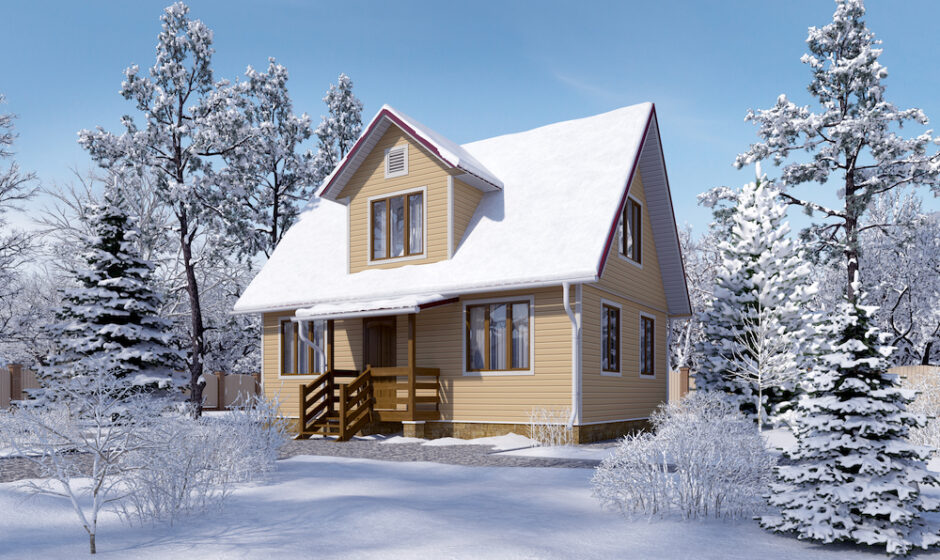
Frame houses are considered one of the most economical in terms of heating costs. However, sometimes in winter a draft and discomfort are felt in the “framework” and you have to significantly increase the heating power. What is the reason and how to prevent heat loss?
A frame wall of a modern design (in this article we will talk only about the “classic” frame wall, without touching on houses made of SIP panels ) perfectly protects from the cold, however, a contracting company may use outdated technologies, low-quality materials or make mistakes when assembling a house. Here are typical examples of construction defects.
1. Incorrect insulation thickness selected
The obvious, but at the same time the most common reason that the house is cold in winter. The required thickness of mineral wool in walls is 150 mm or more, meanwhile, for the sake of economy, they are often limited to a thickness of 100 mm. Unfortunately, sometimes representatives of construction companies are in no hurry to explain that budget houses are aimed exclusively at seasonal living.
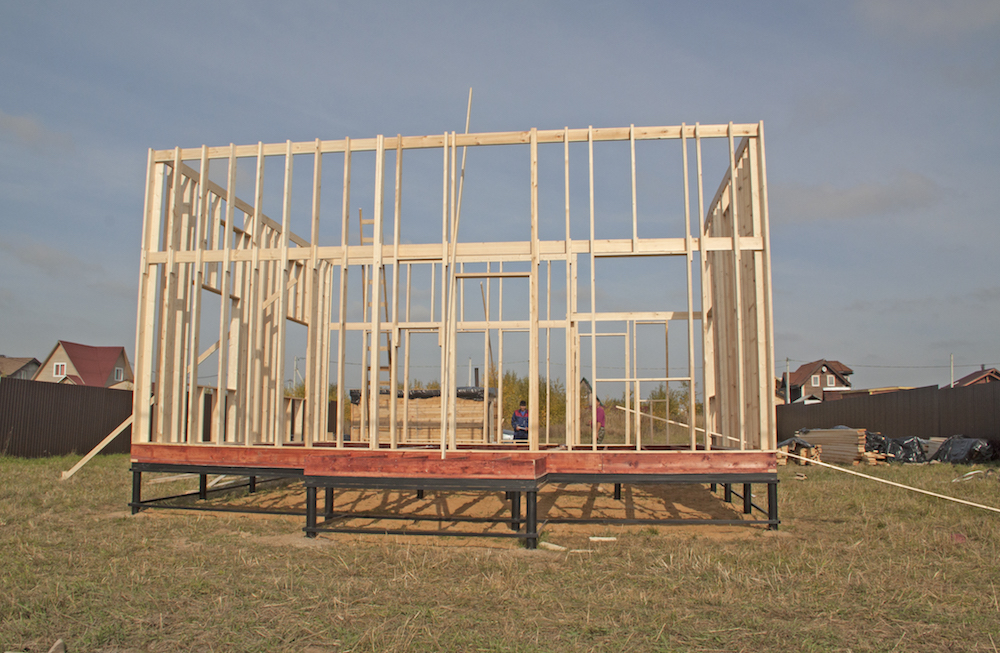

2. The dimensions of the insulation boards do not correspond to the frame cells
This is a gross defect. To speed up construction, mineral wool slabs are cut by eye and quickly covered with finishing. With this approach, voids are inevitable in the design, which become cold bridges and sources of drafts.
Installation of insulation is a hidden work that is subject to mandatory control by the owner or an invited independent specialist (architect, representative of an expert firm). We emphasize that when assembling a classic “frame”, foam plastic is not used, the slabs of which are almost impossible to install in the cells of the frame without gaps (or it is necessary to provide gaps and fill them with polyurethane foam).
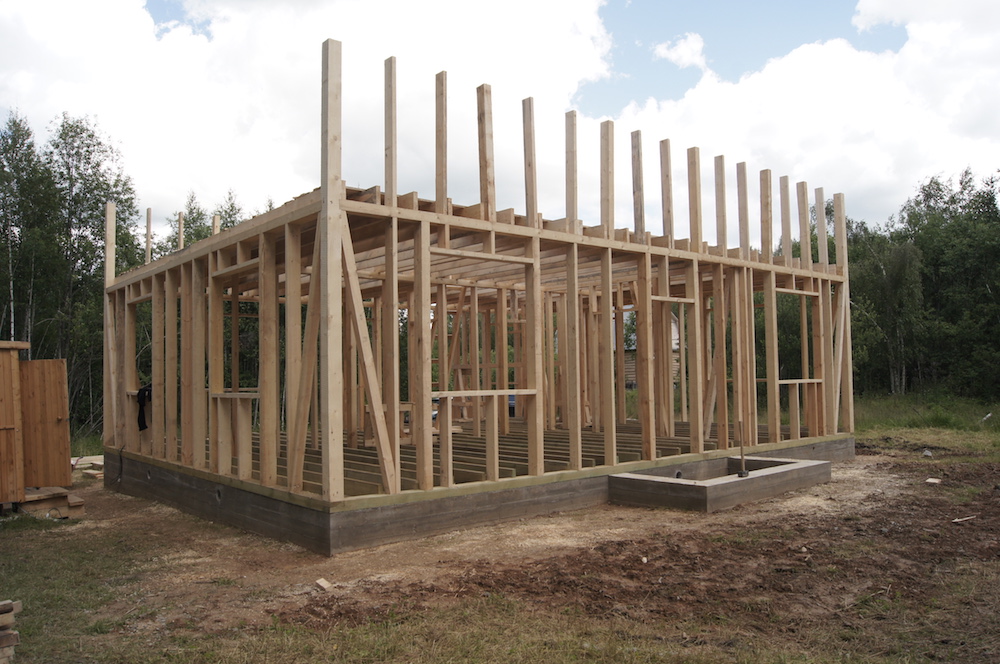

3. The frame posts are warped
If the frame is made of damp, low-grade boards that do not fit well together and are not fastened rigidly enough, the racks may “screw”, which will cause air to blow through the walls.
Avoiding the problem is not so difficult – just buy kiln-dried lumber or purchase in advance grade A boards of natural humidity and dry them in a stack under the roof for a couple of months.
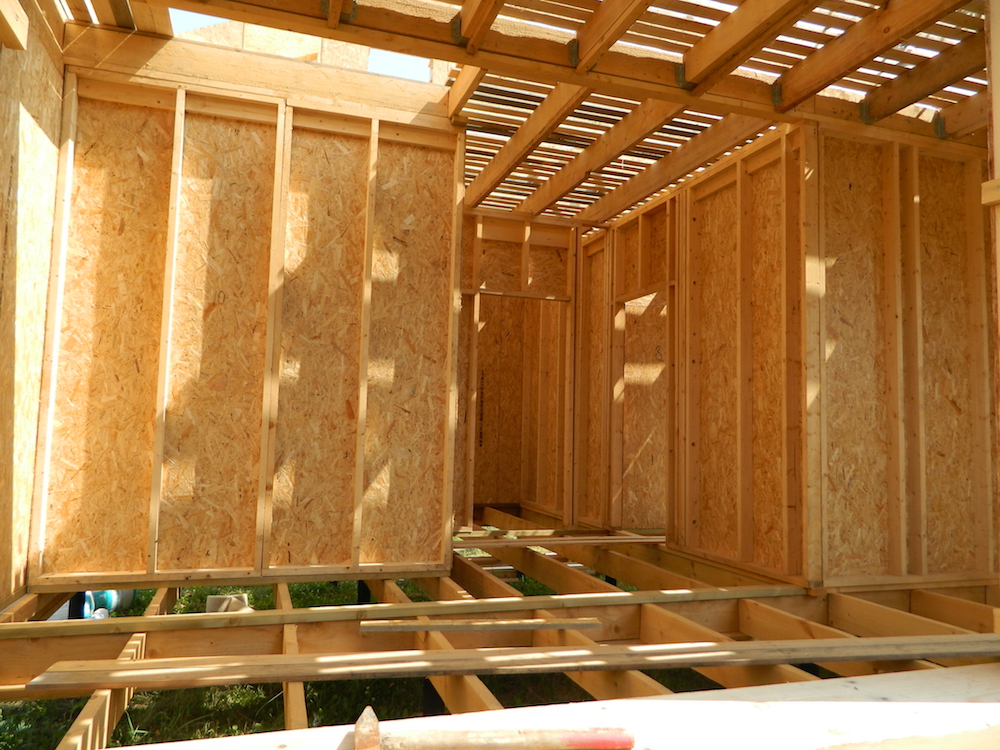

4. Angles are not done correctly
To strengthen the frame, racks made of 150×150 mm timber are sometimes placed in the corners. From the point of view of rigidity and strength (load-bearing capacity), this is unnecessary, but the risk of corner freezing increases, since the thermal conductivity of wood is almost twice that of mineral wool, while the corner in any building is the zone of greatest heat loss.
The corner post should be made hollow (in the form of a box) and filled with insulation.
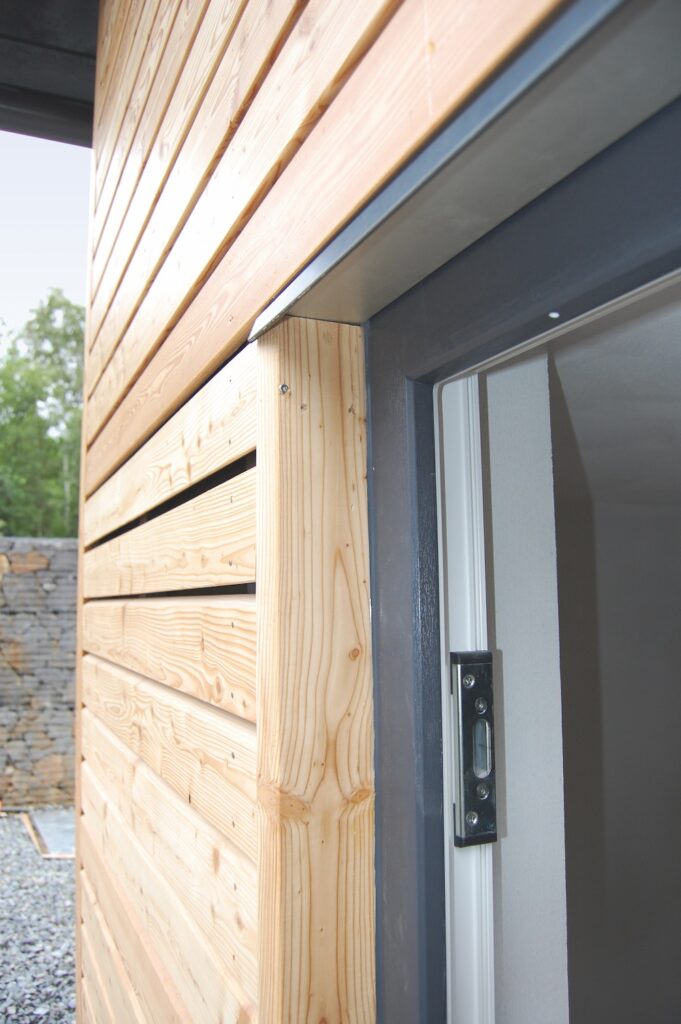

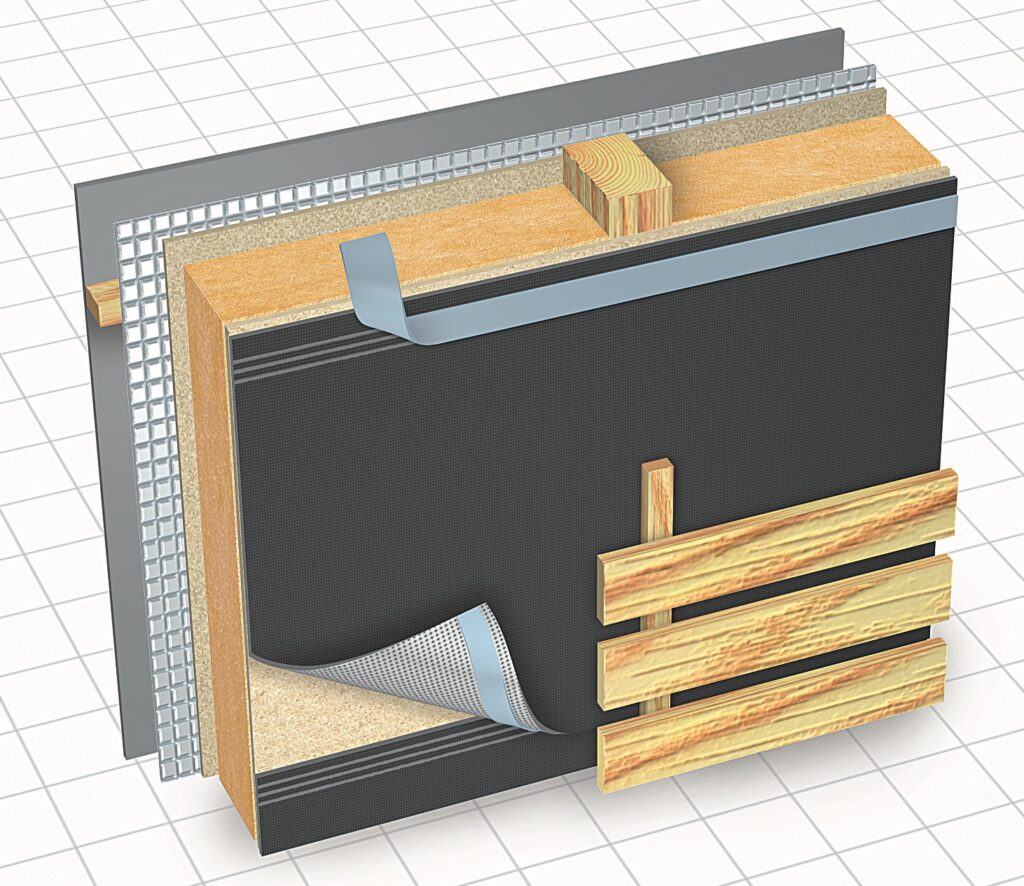
5. There is no wind and moisture protection
Sometimes workers neglect wind protection, relying entirely on sheet sheathing, or using cheap glassine instead of durable modern membranes. Meanwhile, sheathing sheets can rarely be perfectly matched to each other. The result is blowing through the wall.
It is better not to skimp on the water-proof membrane, or it is necessary to seal the OSB joints with sealant, and then cover the entire surface of the slabs with a water-repellent composition.
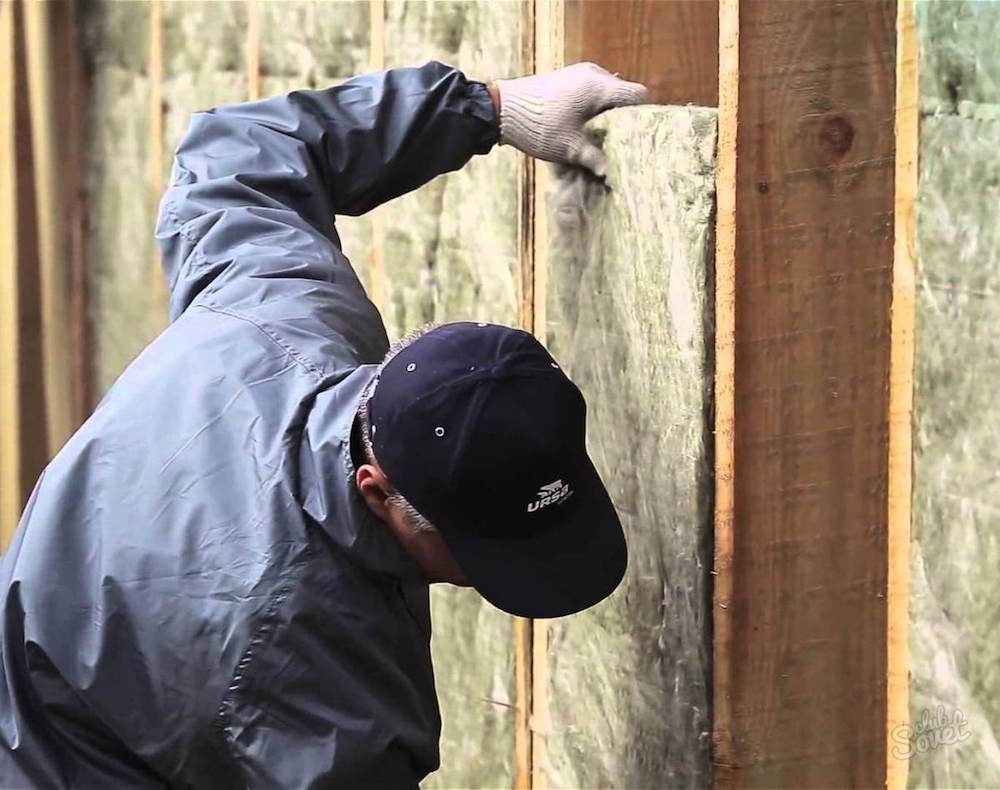

6. The insulation
Poor-quality insulation materials lose their elasticity over time and become deformed – they settle inside the wall. You should buy only specialized facade products, the composition and structure of which ensure stability of shape for decades.
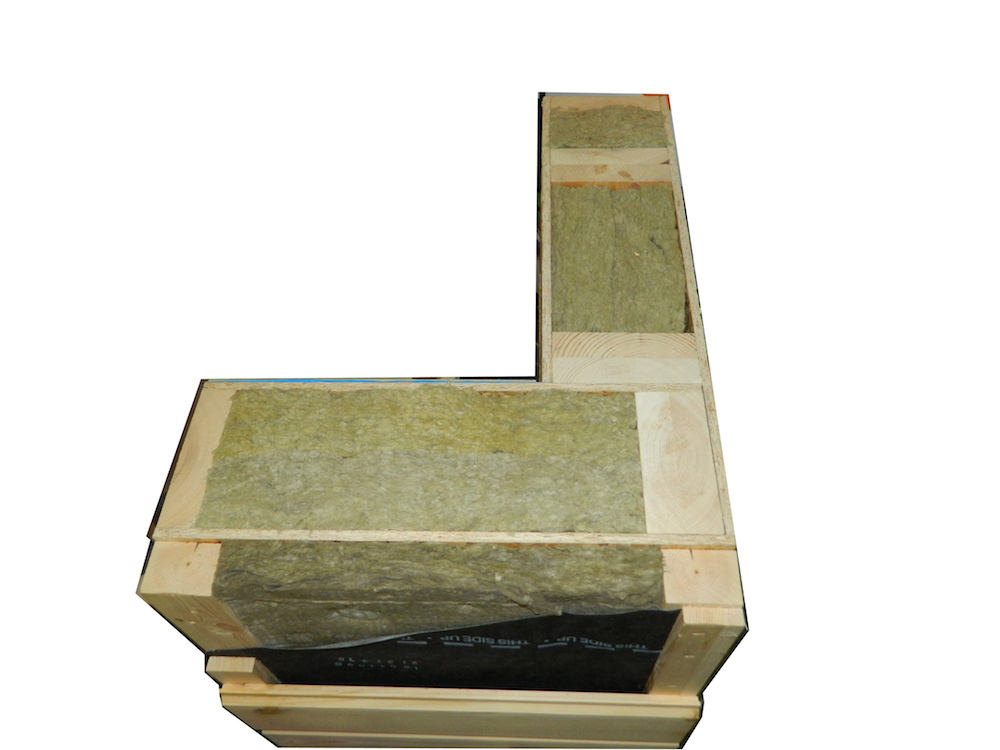
7. The insulation is damp
Moisture can penetrate into the insulation both from the street side (if there is insufficient overlap of the wind and moisture protection strips) and from the room side (if the vapor barrier film is carelessly secured or damaged during the installation of pipes, cables, sockets, etc.). The integrity and tightness of the protective layers must be monitored before finishing begins.

8. Communications are laid in the thickness of the external walls
Gaps and grooves made in the insulation for laying cables and pipes sometimes become the cause of local freezing of the walls, especially if not only the heat but also the vapor barrier layer is damaged (clause 7).
Communications in a frame house are laid in grooves of two-layer plasterboard finishing, in interior partitions, under the floor.
Important Note
The cause of thermal discomfort in a frame house that is not equipped with a ventilation system may be increased relative humidity. With humidity over 75%, 22 degrees feels like 18-19.



